Challenge Yourself with the World's Most Realistic SPLK-1002 Test.
Topic 2: Questions Set 2
Based on the macro definition shown below, what is the correct way to execute the macro in a search string?
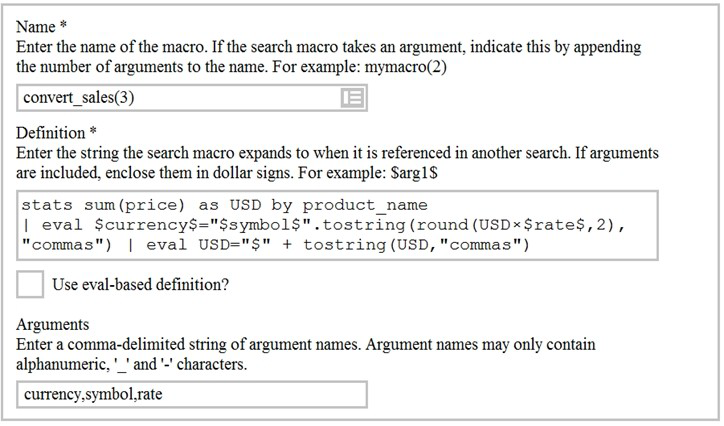
A. Convert_sales (euro, €, 79)”
B. Convert_sales (euro, €, .79)
C. Convert_sales ($euro,$€$,s79$
D. Convert_sales ($euro, $€$,S,79$)
The correct way to execute the macro in a search string is to use the format macro_name($arg1$, $arg2$, ...) where $arg1$, $arg2$, etc. are the arguments for the macro. In this case, the macro name is convert_sales and it takes three arguments: currency, symbol, and rate. The arguments are enclosed in dollar signs and separated by commas. Therefore, the correct way to execute the macro is convert_sales($euro$, $€$, .79).
How does a user display a chart in stack mode?
A. By using the stack command.
B. By turning on the Use Trellis Layout option.
C. By changing Stack Mode in the Format menu.
D. You cannot display a chart in stack mode, only a timechart.
Explanation: A chart is a graphical representation of your search results that shows the relationship between two or more fields2. You can display a chart in stack mode by changing the Stack Mode option in the Format menu2. Stack mode allows you to stack multiple series on top of each other in a chart to show thecumulative values of each series2. Therefore, option C is correct, while options A, B and D are incorrect because they are not ways to display a chart in stack mode.
Which of the following knowledge objects represents the output of an eval expression?
A. Eval fields
B. Calculated fields
C. Field extractions
D. Calculated lookups
The eval command is used to create new fields or modify existing fields based on an expression2. The output of an eval expression is a calculated field, which is a field that you create based on the value of another field or fields2. You can use calculated fields to enrich your data with additional information or to transform your data into a more useful format2. Therefore, option B is correct, while options A, C and D are incorrect because they are not names of knowledge objects that represent the output of an eval expression.
What does the transaction command do?
A. Groups a set of transactions based on time.
B. Creates a single event from a group of events.
C. Separates two events based on one or more values.
D. Returns the number of credit card transactions found in the event logs.
Explanation: The transaction command is a search command that creates a single event from a group of events that share some common characteristics. The transaction command can group events based on fields, time, or both. The transaction command can also create some additional fields for each transaction, such as duration, eventcount, startime, etc. The transaction command does not group a set of transactions based on time, but rather groups a set of events into a transaction based on time. The transaction command does not separate two events based on one or more values, but rather joins multiple events based on one or more values. The transaction command does not return the number of credit card transactions found in the event logs, but rather creates transactions from the events that match the search criteria.
The Field Extractor (FX) is used to extract a custom field. A report can be created using this custom field. The created report can then be shared with other people in the organization. If another person in the organization runs the shared report and no results are returned, why might this be? (select all that apply)
A. Fast mode is enabled.
B. The dashboard is private.
C. The extraction is private-
D. The person in the organization running the report does not have access to the index.
Explanation: The Field Extractor (FX) is a tool that helps you extract fields from your events using a graphical interface2. You can create a report using a custom field extracted by the FX and share it with other users in your organization2. However, if another user runs the shared report and no results are returned, there could be two possible reasons. One reason is that the extraction is private, which means that only you can see and use the extracted field2. To make the extraction available to other users, you need to make it global or app-level2. Therefore, option C is correct. Another reason is that the other user does not have access to the index where the events are stored2. To fix this issue, you need to grant the appropriate permissions to the other user for the index2. Therefore, option D is correct. Options A and B are incorrect because they are not related to the field extraction or the report.
A field alias has been created based on an original field. A search without any transforming commands is then executed in Smart Mode. Which field name appears in the results?
A. Both will appear in the All Fields list, but only if the alias is specified in the search.
B. Both will appear in the Interesting Fields list, but only if they appear in at least 20 percent of events.
C. The original field only appears in All Fields list and the alias only appears in the Interesting Fields list.
D. The alias only appears in the All Fields list and the original field only appears in the Interesting Fields list.
Explanation: A field alias is a way to assign an alternative name to an existing field without changing the original field name or value2. You can use field aliases to make your field names more consistent or descriptive across different sources or sourcetypes2. When you run a search without any transforming commands in Smart Mode, Splunk automatically identifies and displays interesting fields in your results2. Interesting fields are fields that appear in at least 20 percent of events or have high variability among values2. If you have created a field alias based on an original field, both the original field name and the alias name will appear in the Interesting Fields list if they meet these criteria2. However, only one of them will appear in each event depending on which one you have specified in your search string2. Therefore, option B is correct, while options A, C and D are incorrect.
Data model fields can be added using the Auto-Extracted method. Which of the following statements describe Auto-Extracted fields? (select all that apply)
A. Auto-Extracted fields can be hidden in Pivot.
B. Auto-Extracted fields can have their data type changed.
C. Auto-Extracted fields can be given a friendly name for use in Pivot.
D. Auto-Extracted fields can be added if they already exist in the dataset with constraints.
Explanation: Auto-Extracted fields in Splunk Data Models are derived directly from the
indexed data based on the existing fields within the events. These fields are identified and
extracted by Splunk automatically, without the need for explicit field extractions configured
by the user. Understanding the characteristics of Auto-Extracted fields is crucial for
effectively managing Data Models and utilizing them in Pivot tables for analysis.
A. Auto-Extracted fields can be hidden in Pivot. This is true. When building a Data
Model, you have the option to hide certain fields from appearing in Pivot, making the Pivot
tablecleaner and more focused on the fields that are most relevant for analysis. This helps
in reducing clutter and focusing on the data that matters most to the users.
B. Auto-Extracted fields can have their data type changed. This statement is not typically
accurate for Auto-Extracted fields. The data type of an Auto-Extracted field is determined
by Splunk based on the field's content in the indexed data. While you can assign a type to
a field when you manually create a field in a data model, the inherent data type of Auto-
Extracted fields is not something that is changed within the Data Model itself.
C. Auto-Extracted fields can be given a friendly name for use in Pivot. This is correct.
Within Data Models, you can assign a more user-friendly, descriptive name to an Auto-
Extracted field. This feature is particularly useful in making Data Models more intuitive and
easier to use for those who may not be familiar with the original field names or when the
original field names are not descriptive or user-friendly.
D. Auto-Extracted fields can be added if they already exist in the dataset with
constraints. This is true. Auto-Extracted fields are based on fields that already exist in the
data. When you define a dataset within a Data Model, you can apply constraints to narrow
down the events that the dataset includes. The Auto-Extracted fields are then identified
from this constrained dataset. This means that the fields must already be present in the
data that meets the dataset's constraints to be available for auto-extraction.
In summary, Auto-Extracted fields in Splunk Data Models offer a flexible and efficient way
to utilize existing data fields within Pivot tables, with options to rename them for clarity and
hide unnecessary fields to streamline data analysis.
What is the relationship between data models and pivots?
A. Data models provide the datasets for pivots.
B. Pivots and data models have no relationship.
C. Pivots and data models are the same thing.
D. Pivots provide the datasets for data models.
Explanation: The relationship between data models and pivots is that data models provide the datasets for pivots. Data models are collections of datasets that represent your data in a structured and hierarchical way. Data models define how your data is organized into objects and fields. Pivots are user interfaces that allow you to create data visualizations that present different aspects of a data model. Pivots let you select options from menus and forms to create charts, tables, maps, etc., without writing any SPL code. Pivots use datasets from data models as their source of data. Pivots and data models are not the same thing, as pivots are tools for visualizing data models. Pivots do not provide datasets for data models, but rather use them as inputs. Therefore, only statement A is true about the relationship between data models and pivots.
Which of the following statements describe the Common Information Model (CIM)? (select all that apply)
A. CIM is a methodology for normalizing data.
B. CIM can correlate data from different sources.
C. The Knowledge Manager uses the CIM to create knowledge objects.
D. CIM is an app that can coexist with other apps on a single Splunk deployment.
The Common Information Model (CIM) is a methodology for normalizing data from different sources and making it easier to analyze and report on it3. The CIM defines a common set of fields and tags for various domains such as Alerts, Email, Database, Network Traffic, Web and more3. One of the statements that describe the CIM is that it is a methodology for normalizing data, which means that it provides a standard way to name and structure data from different sources so that they can be compared and correlated3. Therefore, option A is correct. Another statement that describes the CIM is that it can correlate data from different sources, which means that it enables you to run searches and reports across data from different sources that share common fields and tags3. Therefore, option B is correct. Another statement that describes the CIM is that the Knowledge Manager uses the CIM tocreate knowledge objects, which means that the person who is responsible for creating and managing knowledge objects such as data models, field aliases, tags and event types can use the CIM as a guide to make their knowledge objects consistent and compatible with other apps and add-ons3. Therefore, option C is correct. Option D is incorrect because it does not describe the CIM but rather one of its components.
Which of the following workflow actions can be executed from search results? (select all that apply)
A. GET
B. POST
C. LOOKUP
D. Search
Explanation: As mentioned before, there are two types of workflow actions: GET and POST1. Both types of workflow actions can be executed from search results by clicking on an event field value that has a workflow action configured for it1. Another type of workflow action is Search, which runs another search based on the field value1. Therefore, options A, B and D are correct, while option C is incorrect because LOOKUP is not a type of workflow action.
| Page 3 out of 28 Pages |
| Splunk SPLK-1002 Dumps Home | Previous |