Challenge Yourself with the World's Most Realistic SPLK-1002 Test.
Topic 2: Questions Set 2
Which of the following searches show a valid use of macro? (Select all that apply)
A. index=main source=mySource oldField=* |'makeMyField(oldField)'| table _time newField
B. index=main source=mySource oldField=* | stats if('makeMyField(oldField)') | table _time newField
C. index=main source=mySource oldField=* | eval newField='makeMyField(oldField)'| table _time newField
D. index=main source=mySource oldField=* | "'newField('makeMyField(oldField)')'" | table _time newField
To use a macro in a search, you must enclose the macro name and any arguments in single quotation marks1. For example, 'my_macro(arg1,arg2)' is a valid way to use a macro with two arguments. You can use macros anywhere in your search string where you would normally use a search command or expression1. Therefore, options A and C are valid searches that use macros, while options B and D are invalid because they do not enclose the macros in single quotation marks.
Which of the following statements describe the search below? (select all that apply)
Index=main I transaction clientip host maxspan=30s maxpause=5s
A. Events in the transaction occurred within 5 seconds.
B. It groups events that share the same clientip and host.
C. The first and last events are no more than 5 seconds apart.
D. The first and last events are no more than 30 seconds apart.
Explanation: The search below groups events by two or more fields (clientip and host),
creates transactions with start and end constraints (maxspan=30s and maxpause=5s), and
calculates the duration of each transaction.
index=main | transaction clientip host maxspan=30s maxpause=5s
The search does the following:
It filters the events by the index main, which is a default index in Splunk that
contains all data that is not sent to other indexes.
It uses the transaction command to group events into transactions based on two
fields: clientip and host. The transaction command creates new events from
groups of events that share the same clientip and host values.
It specifies the start and end constraints for the transactions using the maxspan
and maxpause arguments. The maxspan argument sets the maximum time span
between the first and last events in a transaction. The maxpause argument sets
the maximum time span between any two consecutive events in a transaction. In
this case, the maxspan is 30 seconds and the maxpause is 5 seconds, meaning
that any transaction that has a longer time span or pause will be split into multiple
transactions.
It creates some additional fields for each transaction, such as duration,
eventcount, startime, etc. The duration field shows the time span between the first
and last events in a transaction.
To identify all of the contributing events within a transaction that contains at least one REJECT event, which syntax is correct?
A. Index-main | REJECT trans sessionid
B. Index-main | transaction sessionid | search REJECT
C. Index=main | transaction sessionid | whose transaction=reject
D. Index=main | transaction sessionid | where transaction=reject’’
What do events in a transaction have In common?
A. All events In a transaction must have the same timestamp.
B. All events in a transaction must have the same sourcetype.
C. All events in a transaction must have the exact same set of fields.
D. All events in a transaction must be related by one or more fields.
A transaction is a group of events that share some common characteristics, such as fields, time, or both. A transaction can be created by using the transaction command or by defining an event type with transactiontype=true in props.conf. Events in a transaction have one or more fields in common that relate them to each other. For example, you can create a transaction based on JSESSIONID, which is a unique identifier for each user session in web logs. Events in a transaction do not have to have the same timestamp, sourcetype, or exact same set of fields. They only have to share one or more fields that define the transaction.
Which of the following statements about data models and pivot are true? (select all that apply)
A. They are both knowledge objects
B. Data models are created out of datasets called pivots
C. Pivot requires users to input SPL searches on data models.
D. Pivot allows the creation of data visualizations that present different aspects of a data model.
Explanation: Data models and pivot are both knowledge objects in Splunk that allow you to analyze and visualize your data in different ways. Data models are collections of datasets that represent your data in a structured and hierarchical way. Data models define how your data is organized into objects and fields. Pivot is a user interface that allows you to create data visualizations that present different aspects of a data model. Pivot does not require users to input SPL searches on data models, but rather lets them select options from menus and forms. Data models are not created out of datasets called pivots, but rather pivots are created from datasets in data models.
Which of the following statements describe GET workflow actions?
A. GET workflow actions must be configured with POST arguments.
B. Configuration of GET workflow actions includes choosing a sourcetype.
C. Label names for GET workflow actions must include a field name surrounded by dollar signs.
D. GET workflow actions can be configured to open the URT link in the current window or in a new window
Explanation: GET workflow actions are custom actions that open a URL link when you click on a field value in your search results. GET workflow actions can be configured with various options, such as label name, base URL, URI parameters, app context, etc. One of the options is to choose whether to open the URL link in the current window or in a new window. GET workflow actions do not have to be configured with POST arguments, as they use GET method to send requests to web servers. Configuration of GET workflow actions does not include choosing a sourcetype, as they do not generate any data in Splunk. Label names for GET workflow actions must include a field name surrounded by dollar signs, as this indicates the field value that will be used to replace the variable in the URL link.
Which of the following can be used with the eval command tostring function (select all that apply)
A. ‘’hex’’
B. ‘’commas’’
C. ‘’Decimal’’
D. ‘’duration’’
Explanation:
https://docs.splunk.com/Documentation/Splunk/8.1.0/SearchReference/ConversionFunctio
ns#tostring.28X.2CY.29
The tostring function in the eval command converts a numeric value to a string value. It can
take an optional second argument that specifies the format of the string value. Some of the
possible formats are:
hex: converts the numeric value to a hexadecimal string.
commas: adds commas to separate thousands in the numeric value.
duration: converts the numeric value to a human-readable duration string, such as
“2h 3m 4s”.
Therefore, the formats A, B, and D can be used with the tostring function.
Given the macro definition below, what should be entered into the Name and Arguments fileds to correctly configured the macro?
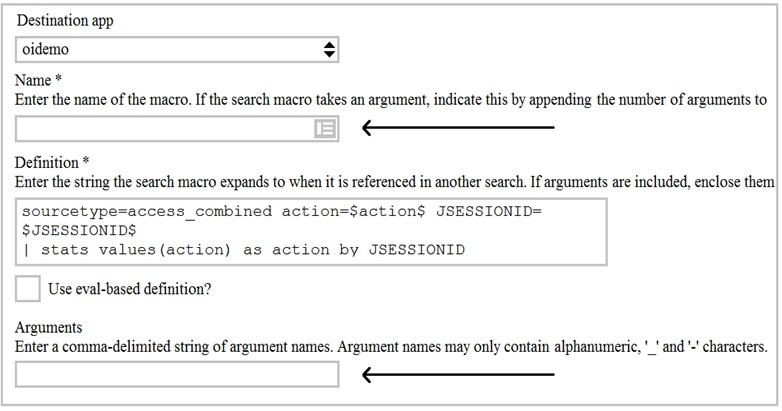
A. The macro name issessiontrackerand the arguments areaction, JESSIONID.
B. The macro name issessiontracker(2)and the arguments areaction, JESSIONID.
C. The macro name issessiontrackerand the arguments are$action$, $JESSIONID$.
D. The macro name issessiontracker(2)and the Arguments are$action$, $JESSIONID$.
The macro definition below shows a macro that tracks user sessions based on two
arguments: action and JSESSIONID.
sessiontracker(2)
The macro definition does the following:
It specifies the name of the macro as sessiontracker. This is the name that will be used to
execute the macro in a search string.
It specifies the number of arguments for the macro as 2. This indicates that the macro
takes two arguments when it is executed.
It specifies the code for the macro asindex=main sourcetype=access_combined_wcookie
action=$action$ JSESSIONID=$JSESSIONID$ | stats count by JSESSIONID. This is the
search string that will be run when the macro is executed. The search string can contain
any part of a search, such as search terms, commands, arguments, etc. The search string
can also include variables for the arguments using dollar signs around them. In this case,
action and JSESSIONID are variables for the arguments that will be replaced by their
values when the macro is executed.
Therefore, to correctly configure the macro, you should enter sessiontracker as the name and action, JSESSIONID as the arguments. Alternatively, you can use sessiontracker(2) as
the name and leave the arguments blank.
When should you use the transaction command instead of the scats command?
A. When you need to group on multiple values.
B. When duration is irrelevant in search results. .
C. When you have over 1000 events in a transaction.
D. When you need to group based on start and end constraints.
Explanation: The transaction command is used to group events into transactions based on some common characteristics, such as fields, time, or both. The transaction command can also specify start and end constraints for the transactions, such as a field value that indicates the beginning or the end of a transaction. The stats command is used to calculate summary statistics on the events, such as count, sum, average, etc. The stats command cannot group events based on start and end constraints, but only on fields or time buckets. Therefore, the transaction command should be used instead of the stats command when you need to group events based on start and end constraints.
Which delimiters can the Field Extractor (FX) detect? (select all that apply)
A. Tabs
B. Pipes
C. Spaces
D. Commas
The Field Extractor (FX) is a tool that helps you extract fields from your data using delimiters or regular expressions. Delimiters are characters or strings that separate fields in your data. The FX can detect some common delimiters automatically, such as pipes (|), spaces ( ), commas (,), semicolons (;), etc.The FX cannot detect tabs (\t) as delimiters automatically, but you can specify them manually in the FX interface.
| Page 5 out of 28 Pages |
| Splunk SPLK-1002 Dumps Home | Previous |