Challenge Yourself with the World's Most Realistic SPLK-1002 Test.
Topic 2: Questions Set 2
Which of the following statements would help a user choose between the transaction and stats commands?
A. state can only group events using IP addresses.
B. The transaction command is faster and more efficient.
C. There is a 1000 event limitation with the transaction command.
D. Use state when the events need to be viewed as a single event.
The transaction command is used to group events that share a common value for one or more fields into transactions3. The transaction command has a default limit of 1000 events per transaction, which means that it will not group more than 1000 events into a single transaction3. This limit can be changed by using the maxevents parameter, but it can affect the performance and memory usage of Splunk3. Therefore, option C is correct, while options A, B and D are incorrect because they are not statements that would help a user choose between the transaction and stats commands.
Complete the search, …. | _____ failure>successes
A. Search
B. Where
C. If
D. Any of the above
Explanation: The where command can be used to complete the search below.
… | where failure>successes
The where command is a search command that allows you to filter events based on
complex or custom criteria. The where command can use any boolean expression or
function to evaluate each event and determine whether to keep it or discard it. The where
command can also compare fields or perform calculations on fields using operators such
as >, <, =, +, -, etc. The where command can be used after any transforming command that
creates a table or a chart.
The search string below does the following:
It uses … to represent any search criteria or commands before the where
command.
It uses the where command to filter events based on a comparison between two
fields: failure and successes.
It uses the greater than operator (>) to compare the values of failure and
successes fields for each event.
It only keeps events where failure is greater than successes.
Which of the following expressions could be used to create a calculated field called gigabytes?
A. eval sc_bytes(1024/1024)
B. | eval negabytes=sc_bytes(1024/1024)
C. megabytes=sc_bytes(1024/1024)
D. sc_bytas(1024/1024)
Which syntax will find events where the values for the 1 field match the values for the Renewal-MonthYear field?
A. | where 10yearAnnerversary=Renewal-MonthYear
B. | where ‘10yearAnnerversary=Renewal-MonthYear
C. | where 10yearAnnerversary=’Renewal-MonthYear’
D. | where ‘10yearAnnerversary’=’Renewal-MonthYear’
Explanation: The correct answer is A. | where 10yearAnnerversary=Renewal-MonthYear.
The where command is used to filter the search results based on an expression that
evaluates to true or false. The where command can compare two fields, two values, or a
field and a value. The where command can also use functions, operators, and wildcards to
create complex expressions1.
The syntax for the where command is:
| where
The expression can be a comparison, a calculation, a logical operation, or a combination of
these. The expression must evaluate to true or false for each event.
To compare two fields with the where command, you need to use the field names without
any quotation marks. For example, if you want to find events where the values for the
10yearAnnerversary field match the values for the Renewal-MonthYear field, you can use
the following syntax:
| where 10yearAnnerversary=Renewal-MonthYear
This will return only the events where the two fields have the same value.
The other options are not correct because they use quotation marks around the field
names, which will cause the where command to interpret them as string values instead of
field names. For example, if you use:
| where ‘10yearAnnerversary’=‘Renewal-MonthYear’
This will return no events because there are no events where the string value
‘10yearAnnerversary’ is equal to the string value ‘Renewal-MonthYear’.
When does the CIM add-on apply preconfigured data models to the data?
A. Search time
B. Index time
C. On a cron schedule
D. At midnight
Explanation: The Common Information Model (CIM) add-on in Splunk applies preconfigured data models to data at search time. This means that when a search is executed, the CIM add-on uses its predefined data models to normalize and map the relevant data to a common format. This approach ensures that data is interpreted and analyzed consistently across various datasets without modifying the data at index time.
Using the Field Extractor (FX) tool, a value is highlighted to extract and give a name to a new field. Splunk has not successfully extracted that value from all appropriate events. What steps can be taken so Splunk successfully extracts the value from all appropriate events? (select all that apply)
A. Select an additional sample event with the Field Extractor (FX) and highlight the missing value in the event.
B. Re-ingest the data and attempt to extract from a new dataset.
C. Click on the event where the field was not extracted and choose “Change to Delimited".
D. Edit the regular expression manually.
Explanation:
When using the Field Extractor (FX) tool in Splunk and the tool fails to extract a value from
all appropriate events, there are specific steps you can take to improve the extraction
process. These steps involve interacting with the FX tool and possibly adjusting the
extraction method:
A. Select an additional sample event with the Field Extractor (FX) and highlight the
missing value in the event. This approach allows Splunk to understand the pattern better
by providing more examples. By highlighting the value in another event where it wasn't
extracted, you help the FX tool to learn the variability in the data format or structure,
improving the accuracy of the field extraction.
D. Edit the regular expression manually. Sometimes the FX tool might not generate the
most accurate regular expression for the field extraction, especially when dealing with
complex log formats or subtle nuances in the data. In such cases, manually editing the
regular expression can significantly improve the extraction process. This involves
understanding regular expression syntax and how Splunk extracts fields, allowing for a
more tailored approach to field extraction that accounts for variations in the data that the
automatic process might miss.
Options B and C are not typically related to improving field extraction within the Field
Extractor tool. Re-ingesting data (B) does not directly impact the extraction process, and
changing to a delimited extraction method (C) is not always applicable, as it depends on
the specific data format and might not resolve the issue of missing values across events.
Two separate results tables are being combined using the |join command. The outer table
has the following values:
Refer to following Tables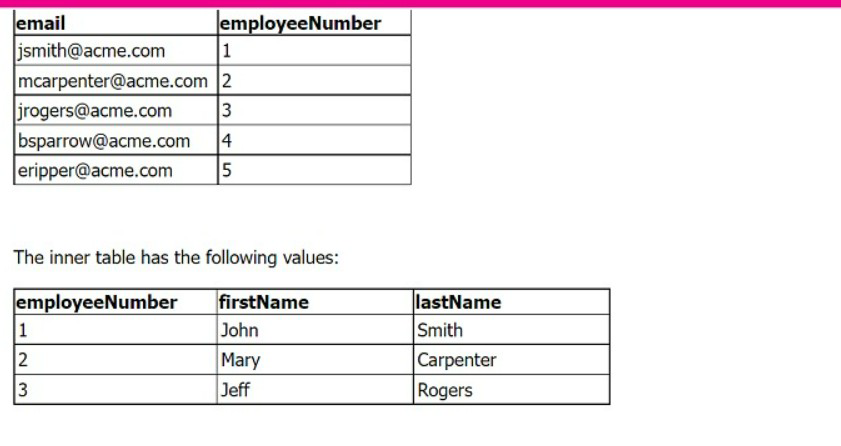
The line of SPL used to join the tables is: | join employeeNumber type=outer
How many rows are returned in the new table?
A. Zero
B. Five
C. Eight
D. Three
Explanation:
When performing an outer join in Splunk using the | join employeeNumber
type=outer command, it combines the rows from both tables based on
the employeeNumber field. An outer join returns all rows from both tables, with matching
rows from both sides where available. If there is no match, the result is NULL on the side of
the join where there is no match.
In the provided tables, there are five rows in the first table and three in the second. Since
it’s an outer join, all rows from both tables will be returned. This means the new table will
have a total of eight rows, combining the matched rows and the unmatched rows from both
tables.
Which option of the transaction command would be used to specify the maximum time between events in a transaction?
A. maxpause
B. maxspan
C. duration
D. eventcount
Explanation: The maxpause option of the transaction command in Splunk is used to specify the maximum time allowed between events in a transaction. If the time between events exceeds the maxpause value, those events are not considered part of the same transaction.
Which of the following describes the I transaction command?
A. It is an SPL command that groups at least two events together based on shared values in selected fields.
B. It allows an exchange of data from one Splunk index to another Splunk index.
C. It is an SPL command that groups events together with shared values in selected fields.
D. It allows an exchange of data from one Splunk system to another Splunk system.
Explanation:
The transaction command is a Splunk command that finds transactions based on
events that meet various constraints.
Transactions are made up of the raw text (the _raw field) of each member, the
time and date fields of the earliest member, as well as the union of all other fields
of each member.
The transaction command groups events together by matching one or more fields
that have the same value across the events . For example, | transaction
clientip will group events that have the same value in the clientip field.
Which of the following about reports is/are true?
A. Reports are knowledge objects.
B. Reports can be scheduled.
C. Reports can run a script
D. All of the above
Explanation: A report is a way tosave a search and its results in a format that you can reuse and share with others2. A report is also a type of knowledge object, which is an entity that you create to add knowledge to your data and make it easier to search and analyze2. Therefore, option A is correct. A report can be scheduled, which means that you can configure it to run at regular intervals and send the results to yourself or others via email or other methods2. Therefore, option B is correct. A report canrun a script, which means that you can specify a script file to execute when the report runs and use it to perform custom actions or integrations2. Therefore, option C is correct. Therefore, option D is correct because all of the above statements are true for reports.
| Page 8 out of 28 Pages |
| Splunk SPLK-1002 Dumps Home | Previous |