Challenge Yourself with the World's Most Realistic SPLK-1003 Test.
What options are available when creating custom roles? (select all that apply)
A. Restrict search terms
B. Whitelist search terms
C. Limit the number of concurrent search jobs
D. Allow or restrict indexes that can be searched.
Explanation:
When creating custom roles in Splunk, you can configure the following permissions and restrictions:
Restrict Search Terms (A):
Use srchFilter in authorize.conf to limit searches to specific patterns (e.g., block sourcetype=password).
Limit Concurrent Search Jobs (C):
Set srchJobsQuota to control how many simultaneous searches a role can run.
Allow/Restrict Indexes (D):
Define srchIndexesAllowed or srchIndexesDefault to specify accessible indexes.
Why Not B (Whitelist Search Terms)?
Splunk supports blocking terms (blacklisting) via srchFilter, but not explicit whitelisting.
Whitelisting would require complex workarounds (e.g., search macros with enforced syntax).
Example authorize.conf Settings:
text
[role_custom]
srchIndexesAllowed = main,web_logs
srchJobsQuota = 5
srchFilter = NOT sourcetype=password
Reference:
Splunk Docs: Configure role-based permissions
When running a real-time search, search results are pulled from which Splunk component?
A. Heavy forwarders and search peers
B. Heavy forwarders
C. Search heads
D. Search peers
Explanation:
Using the Splunk reference URLhttps://docs.splunk.com/Splexicon:Searchpeer
"search peer is a splunk platform instance that responds to search requests from a search
head. The term "search peer" is usally synonymous with the indexer role in a distributed
search topology. However, other instance types also have access to indexed data,
particularly internal diagnostic data, and thus function as search peers when they respond
to search requests for that data."
Where should apps be located on the deployment server that the clients pull from?
A. $SFLUNK_KOME/etc/apps
B. $SPLUNK_HCME/etc/sear:ch
C. $SPLUNK_HCME/etc/master-apps
D. $SPLUNK HCME/etc/deployment-apps
Explanation:
To distribute apps to forwarders via the Splunk Deployment Server, you must place them in the deployment-apps directory. Here’s why:
$SPLUNK_HOME/etc/deployment-apps (D):
The correct directory for apps that forwarders (Universal/Heavy Forwarders) pull from the Deployment Server.
Apps here are pushed to clients based on their server class (defined in serverclass.conf).
Why Not Other Options?
A ($SPLUNK_HOME/etc/apps): Stores apps local to the Deployment Server, not for deployment.
B ($SPLUNK_HOME/etc/search): Invalid directory (typo in the option).
C ($SPLUNK_HOME/etc/master-apps): Used for app version control (e.g., with Deployment Client), not forwarder deployment.
Key Workflow:
1. Place the app in deployment-apps.
2. Map the app to a server class in serverclass.conf:
[serverClass:web_servers]
whitelist.0 = host_web*
app.0 = my_custom_app
3. Forwarders in the web_servers class will receive my_custom_app
The Splunk administrator wants to ensure data is distributed evenly amongst the indexers.
To do this, he runs
the following search over the last 24 hours:
index=*
What field can the administrator check to see the data distribution?
A. host
B. index
C. linecount
D. splunk_server
The splunk server field contains the name of the Splunk server containing the event. Useful in a distributed Splunk environment. Example: Restrict a search to the main index on a server named remote. splunk_server=remote index=main 404
What is an example of a proper configuration for CHARSET within props.conf?
A. [host: : server. splunk. com]
CHARSET = BIG5
B. [index: :main]
CHARSET = BIG5
C. [sourcetype: : son]
CHARSET = BIG5
D. [source: : /var/log/ splunk]
CHARSET = BIG5
Explanation: According to the Splunk documentation1, to manually specify a character set
for an input, you need to set the CHARSET key in the props.conf file. You can specify the
character set by host, source, or sourcetype, but not by index.
https://docs.splunk.com/Documentation/Splunk/latest/Data/Configurecharactersetencoding
Which configuration files are used to transform raw data ingested by Splunk? (Choose all that apply.)
A. props.conf
B. inputs.conf
C. rawdata.conf
D. transforms.conf
Use transformations with props.conf and transforms.conf to:
– Mask or delete raw data as it is being indexed
– Override sourcetype or host based upon event values
– Route events to specific indexes based on event content
– Prevent unwanted events from being indexed
Which of the following is a benefit of distributed search?
A. Peers run search in sequence.
B. Peers run search in parallel.
C. Resilience from indexer failure.
D. Resilience from search head failure.
Explanation: https://docs.splunk.com/Documentation/Splunk/8.2.2/DistSearch/Whatisdistributedsearch Parallel reduce search processing If you struggle with extremely large high-cardinality searches, you might be able to apply parallel reduce processing to them to help them complete faster. You must have a distributed search environment to use parallel reduce search processing.
What are the values forhostandindexfor[stanza1]used by Splunk during index time, given the following configuration files?
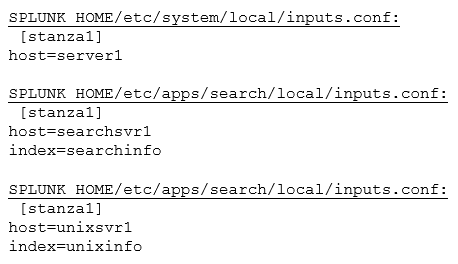
A. host=server1
index=unixinfo
B. host=server1
index=searchinfo
C. host=searchsvr1
index=searchinfo
D. host=unixsvr1
index=unixinfo
Explanation: - etc/system/local/ has better precedence at index time - for identical settings in the same file, the last one overwrite others, see :https://community.splunk.com/t5/Getting-Data-In/What-is-the-precedence-for-identicalstanzas- within-a-single/m-p/283566
When would the following command be used?
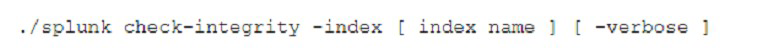
A. To verify' the integrity of a local index.
B. To verify the integrity of a SmartStore index.
C. To verify the integrity of a SmartStore bucket.
D. To verify the integrity of a local bucket.
Explanation: To verify the integrity of a local bucket. The command ./splunk checkintegrity -bucketPath [bucket path] [-verbose] is used to verify the integrity of a local bucket by comparing the hashes stored in the l1Hashes and l2Hash files with the actual data in the bucket1. This command can help detect any tampering or corruption of the data.
Given a forwarder with the following outputs.conf configuration:
[tcpout : mypartner]
Server = 145.188.183.184:9097
[tcpout : hfbank]
server = inputsl . mysplunkhfs . corp : 9997 , inputs2 . mysplunkhfs . corp : 9997
Which of the following is a true statement?
A. Data will continue to flow to hfbank if 145.1 ga. 183.184 : 9097 is unreachable.
B. Data is not encrypted to mypartner because 145.188 .183.184 : 9097 is specified by IP.
C. Data is encrypted to mypartner because 145.183.184 : 9097 is specified by IP.
D. Data will eventually stop flowing everywhere if 145.188.183.184 : 9097 is unreachable.
Explanation:
The outputs.conf file defines how forwarders send data to receivers1. You can
specify some output configurations at installation time (Windows universal
forwarders only) or the CLI, but most advanced configuration settings require that
you edit outputs.conf1.
The [tcpout:…] stanza specifies a group of forwarding targets that receive data
over TCP2. You can define multiple groups with different names and settings2.
The server setting lists one or more receiving hosts for the group, separated by
commas2. If you specify multiple hosts, the forwarder load balances the data
across them2.
Therefore, option A is correct, because the forwarder will send data to both
inputsl.mysplunkhfs.corp:9997 and inputs2.mysplunkhfs.corp:9997, even if
145.188.183.184:9097 is unreachable.
| Page 3 out of 19 Pages |
| Splunk SPLK-1003 Dumps Home | Previous |